LOWER LIMB CONDITIONS
Here you will find a list of lower limb musculoskeletal, dermatological (skin & nail), and paediatric conditions.
Please note; we are continually building the information database.
Conditions that have further information available will have a "read more" link.

Musculoskeletal Conditions
Within this section you will find a comprehensive list of musculoskeletal conditions/injuries that can develop in the foot and lower limb.
They are categorised into _acute and _chronic conditions.
Further divided into sub-categories for; forefoot, midfoot, rearfoot, ankle and lower leg conditions.
Acute Musculoskeletal Conditions
Acute refers to conditions that typically have a sudden onset, often from trauma or an acute loading event (i.e., a single activity or movement), and symptoms typically appear quickly (pain, swelling, inflammation, bruising etc.).
Forefoot
Metatarsal Fractures | Often due to trauma, but can occur due to overuse with an acute loading event*.
Sesamoiditis | Inflammation of the sesamoid bones under the 1st MTPJ (big toe joint). Acute presentations typically occur after a highly-repetitive +/- high-loading activity.
Turf Toe | Sprain of the ligaments and joint capsule under the 1st MTPJ (big toe joint), typically from hyperextension (upward bending).
Sand Toe | Sprain of the ligaments and joint capsule on top of the 1st MTPJ (big toe joint), typically from hyperflexion (downward bending).
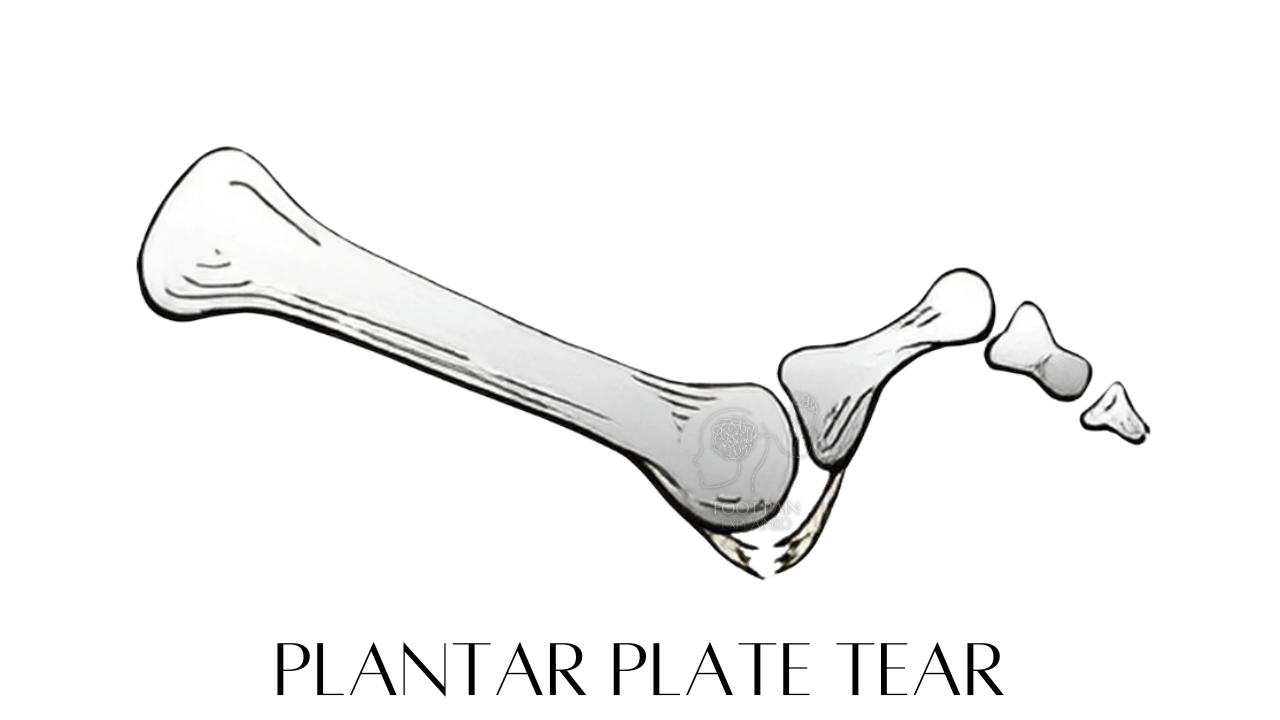
Plantar Plate Tears | Injury to the ligament and connective tissue structures supporting the MTPJs (toe joints), leading to instability of the joints*.
Phalangeal Fractures | Fractures of the toe bones, usually from direct impact.
Sesamoid Fractures | Fractures involving the small bones beneath the big toe joint. Acute fractures are often associated with trauma and other injuries (e.g., "Turf Toe").
Acute Tendon Strains | Injuries to the flexor or extensor tendons of the toes, either due to trauma or hyperflexion or hyperextension injuries.
Acute Synovitis of MTPJ | Inflammation of the metatarsophalangeal joints (toe joints) due to trauma and/or a high-loading event*.
*Metatarsalgia | Pain occurring at the ball of the foot. This is a common diagnosis of forefoot pain, however, similar to plantar heel pain, there is often great variation in what tissues are involved and what is causing the pain between individuals. A more specific diagnosis is typically required.
Nerve Lacerations | Damage to nerves such as the interdigital nerves (between the toes and metatarsals), often from cuts, puncture wounds or severe trauma.


Midfoot
Cuboid Syndrome | This is a condition describing pain occurring at the lateral (outer) aspect of the midfoot. Pain can arise after an acute injury (e.g., lateral ankle sprain) or develop over time.
Much is still unknown about the condition and no specific diagnositic tests exist to confirm the condition. Similar to 'Metatarsalgia', there are likely more specific tissues involved that likely have a more specific diagnosis (e.g., sprain of plantar cuboideonavicular and cuboideometatarsal ligaments that stabilise the cuboid).
Lisfranc Injuries | Sprains (+/- fractures) of the midfoot joints and ligaments, often from twisting, stomping, or hyperflexion injuries.
Midfoot Sprains | Ligament injuries in the midfoot region, typically from falls or sports. These can involve the Lisfranc and/or Chopart joint complexes.
Os Naviculare Syndrome (Acute) | Often a chronic condition, however, inflammation can develop after a high-intensity activity. This occurs at the insertion of the tibialis posterior tendon due to an accessory bone associated with the midfoot bone known as the navicular (Os Naviculare).
Acute Midfoot Fractures | Fractures of the navicular, cuboid and/or cuneiform bones of the midfoot. Acute fractures are often a result of high-load trauma and also typically involve ligament injuries, with potential dislocations.
Acute Joint Dislocations | Displacement of midfoot joints due to high-load trauma. Can involve the Lisfranc and/or Chopart joints. Fractures may commonly occur with midfoot dislocations.
Acute Nerve Trauma | Injuries to nerves like the medial or lateral plantar nerves, often due to trauma, severe fractures and/or puncture wounds.



Rearfoot
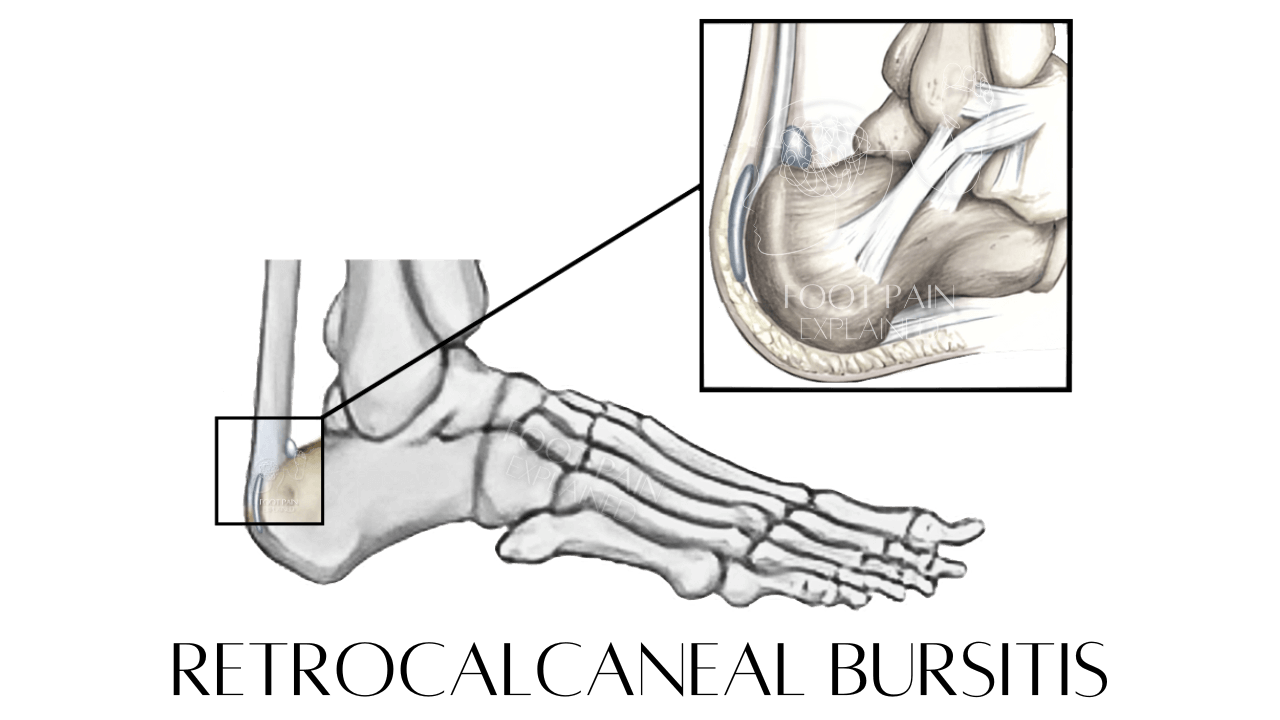
Retrocalcaneal Bursitis | Inflammation of the bursa located between the Achilles tendon insertion and the calcaneus (heel bone). Pain and inflammation can develop acutely, after highly repetitive and/or high loading activities, or develop over time (chronic).
Calcaneal Fractures | Fractures of the heel bone, often from high-impact landings and/or falls.
Talus Fractures | Fractures of the talus (bone connecting the foot and ankle), usually from high-energy injuries (e.g., significant ankle sprain injuries).
Acute Plantar Fascia Tear or Rupture | Sudden full or partial tearing of the plantar fascia.
Bone Contusions | Bruising of bones, often occurs during high impact or significant injuries (e.g., high-grade ankle sprain).
Peroneal Tendon Subluxation | Displacement of the tendons on the outer ankle.
Acute Subtalar Dislocation | Dislocation of the joint below the ankle joint.
Acute Nerve Trauma | Injuries to nerves such as those in the tarsal tunnel.


Ankle
Ankle Sprains | Trauma to ankle ligaments, including; lateral (outer), medial (inner) and syndesmosis (high-ankle) injuries, commonly from "rolling" the ankle.
Tenosynovitis | Acute inflammation of the tendon sheaths that cross the ankle joint.
Achilles tendon
Tibialis posterior
Peroneals
Flexor hallucis longus
Flexor digitorum longus
Achilles Tendon Tear | Partial tear of the Achilles tendon.
Achilles Tendon Rupture | Complete tear of the Achilles tendon.
Distal Fibula Fractures | Fractures of the outer ankle/shin bone due to trauma.
Distal Tibia Fractures | Fractures of the inner ankle/shin bone.
Acute Synovitis | Inflammation of the ankle joint lining due to injury.
Dislocations | Partial or complete displacement of a joint, often occurs concomitantly (at the same time) with fractures. The ankle joint and subtalar joint are two of the most common dislocations that can occur in the foot and ankle.
Nerve Trauma | Injuries to nerves such as the sural or saphenous nerves.



Lower Leg
Calf Muscle Strain | Injuries to muscles like the calf muscle, peroneals or tibialis anterior.
Bone Contusion (Bruise) |
Muscle Contusion (Bruise) |
Acute Compartment Syndrome |
Fibula Fractures (Shaft) |
Tibia Fractures (Shaft) |
Chronic Musculoskeletal Conditions
Acute refers to conditions that typically have a sudden onset, often from trauma or an acute loading event (i.e., a single activity or movement), and symptoms typically appear quickly (pain, swelling, bruising etc.).
Forefoot
Plantar Fasciopathy (Distal) | Chronic heel pain due to degeneration of the plantar fascia.
Morton’s Neuroma | Thickening of tissue around a nerve leading to the toes, causing pain.
Chronic Plantar Plate Insufficiency | Weakening of the ligament supporting the toe joints.
Metatarsal Stress Fractures (Distal) | Stress fractures occurring in the shaft or head of the metatarsal bones.
Hallux Rigidus/Limitus | Stiffness and arthritis of the big toe joint.
Gout | Arthritis caused by uric acid crystal deposits, often in the big toe.
Sesamoiditis | Inflammation of the sesamoid bones beneath the big toe.
Freiberg’s Disease | Avascular necrosis of the metatarsal head, leading to pain.
Midfoot
Lisfranc Injuries | read more
Sprains or fractures of the midfoot joints and ligaments, often from twisting, stomping, or hyperflexion injuries.
Midfoot Sprains | Ligament injuries in the midfoot region, typically from falls or sports.
Can involve the lisfranc joints and/or other joints in the region.
Navicular Fractures |
Fractures of the navicular bone, common in athletes. Acute fractures often associated with trauma and are much rarer than stress fractures.
Cuneiform or Cuboid Fractures |
Fractures of the midfoot bones, very rare. Acute fractures often result from trauma.
Tibialis Posterior Tendonitis or Tenosynovitis |
Inflammation of the tibialis posterior tendon or tendon sheath at its insertion (attachment) point in the midfoot, often a result of a high bout of loading. Can be associated with Os Naviculare (accessory bone).
Acute Nerve Trauma |
Injuries to nerves like the medial or lateral plantar nerves. Acute injuries typically associated with trauma.
Acute Joint Dislocations |
Displacement of midfoot joints due to high-impact trauma. Can be associated with fractures and Lisfranc or Chopart joint injuries.
Rearfoot
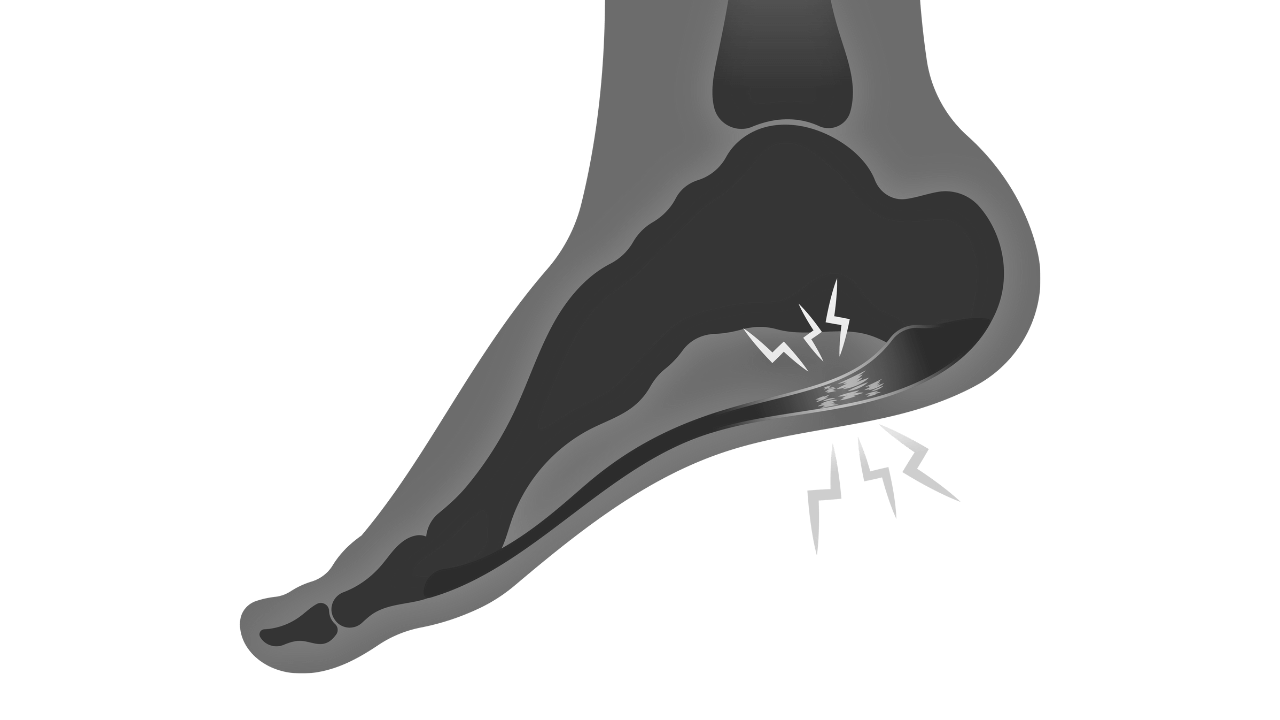
Plantar Fasciopathy | Chronic heel pain caused by degeneration or overuse of the plantar fascia.
Achilles Tendinopathy | Degeneration of the Achilles tendon (either mid-portion or insertional).
Heel Pad Atrophy | Thinning of the fat pad under the heel, causing pain.
Heel Spur | Calcification at the insertion of the plantar fascia, often secondary to chronic plantar fasciopathy.
Peroneal Tendinopathy | Chronic inflammation or degeneration of the peroneal tendons.
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome | Chronic compression of the tibial nerve within the tarsal tunnel.
Calcaneal Stress Fractures | Repetitive stress leading to small fractures in the heel bone.
Osteonecrosis | Loss of blood supply to the talus or calcaneus, leading to bone collapse.
Subtalar Arthritis | Degeneration of the subtalar joint, often post-traumatic or from inflammatory conditions.
Peroneal Tendon Subluxation | Known an "snapping ankle", often resulting from damage to the connective tissues that hold the peroneal tendons in place.
Ankle
Chronic Ankle Instability | Recurring episodes of giving way due to ligament laxity from repeated sprains.
Osteoarthritis | Degeneration of the ankle and/or subtalar joints, often secondary to trauma.
Posterior Tibial Tendinopathy | Chronic degeneration of the posterior tibial tendon affecting foot support.
Peroneal Tendinopathy | Degenerative changes in the peroneal tendons around the ankle.
Stress Fractures | Small fractures in bones such as the talus or distal tibia due to repetitive stress.
Osteochondral Lesions | Damage to the cartilage and underlying bone, can result from trauma/injury and become chronic (often involves the talus).
Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis | Degeneration of the ankle and/or subtalar joints, occurring secondary to trauma/injury.
Rheumatoid Arthritis | Autoimmune joint destruction affecting the ankle.